
What are the symptoms of an oblique fracture? People with osteoporosis (weakened bones) have an increased risk for all types of broken bones, including oblique fractures. If you’re at risk for falls, you might be more likely to experience an oblique fracture. This is especially true because they’re caused by falls or traumas. Oblique fractures - like all bone fractures - can affect anyone. Oblique fractures are one of the most common kinds of broken bones, especially in long bones. No matter which names and terms end up applied to your fracture, the most important first step is getting your injury examined by your healthcare provider as soon as possible. Transverse fractures run horizontally perpendicular to your bone (opposite the direction of your bone). Oblique fractures are angled across your bone. Oblique fractures and transverse fractures both mean the break goes across your bone’s width in a straight line. They’re common in sports injuries when people’s bones are twisted with great force (like getting tackled in football). Spiral fractures happen when a fracture winds around the length of your bone - like a spiral staircase. They’re usually caused by landing on your bone at an angle after a fall, or when your bone is hit suddenly from an angle (like in a car accident). The fracture is a straight line that’s angled across the width of your bone. Oblique fractures occur when your bone is broken at an angle. They are different terms that tell your healthcare provider specific details about how your bones are broken and the shape of the fracture. Oblique fractures and spiral fractures are different types of bone fractures. Most people need a few months to recover from an oblique fracture. How long it takes to recover fully depends on which of your bones are fractured - and what caused the breaks. Some people only need a splint or cast for the bone to heal. You might need surgery to repair your bone. Oblique fractures are almost always caused by falls or other traumas. Oblique fractures usually affect long bones in your body. This means the line of the break goes all the way through your bone. You might see oblique fractures referred to as complete fractures. They happen when one of your bones is broken at an angle. Oblique fractures are a type of broken bone. Thank you for choosing Summit Health.An oblique fracture angles across a bone. Someone will get back to you as soon as possible. If you have sustained a tibia or fibula fracture, follow the link below and answer a few short questions. PT focuses on exercises designed to increase range of motion and strength of the muscles and tissues around the fracture. Rehabilitation and physical therapy (PT) are important parts of healing from a broken tibia or fibula. To manage pain, opioids or anti-inflammatories may be prescribed. A broken tibia heals even more slowly-four to six months or longer. Recovery from a broken fibula may take six weeks or longer. This hardware could be internal (under the skin) or external, such as attached to a bar outside the skin. The surgeon uses plates, screws or rods to hold the broken portions of the bone together. Surgery may be necessary if the fracture does not respond to immobilization, if it is a displaced fracture or if the fracture site has a number of bone fragments. These usually include immobilization with a cast or brace to allow the fracture to heal on its own. TreatmentĪ fibula or tibia fracture can often be treated with conservative measures. An X-ray can detect the presence of a fracture and its severity, and a computed tomography (CT) scan can show if there is any damage to the knee or ankle joints. The doctor usually starts with a medical history to learn about the injury sustained and any other medical problem, and then look for signs and symptoms of a fracture. Athletes in sports with much twisting or cutting, such as basketball or tennis, are especially prone to tibia and fibula fractures. Bone poking through the skin, in the case of a compound fractureĪ fibula or tibia fracture can occur in one of two ways: either a high-energy trauma like a car accident, or a low-energy event like a fall or sports injury.
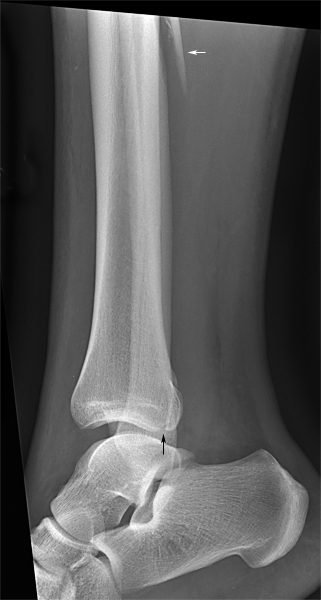
Symptoms of a lower leg fracture include: Fibula fractures often manifest as broken ankles. The tibia is the most often fractured-or broken-long bone in the body (long bones also include the femur, fibula and humerus). The tibia, the larger of the two bones, is the shinbone and is at the front of the leg, while the fibula is known as the calf bone and can be found next to the tibia on the outside of the lower leg. The tibia and fibula are bones in the lower leg.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
